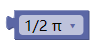数学
| Site: | 聚观点-集成开发环境 |
| Course: | 必修1. 互联网创意编程基础 |
| Book: | 数学 |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Tuesday, 10 March 2026, 10:54 AM |
Table of contents
- 1. 表达式
- 2. 数值
- 3. 向量
- 3.1. 向量xyz
- 3.2. 向量设置
- 3.3. 向量复制
- 3.4. 向量相加xyz
- 3.5. 向量相加ab
- 3.6. 向量求余xyz
- 3.7. 向量求余ab
- 3.8. 向量相减xyz
- 3.9. 向量相减ab
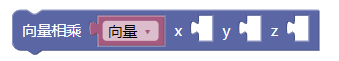
- 3.10. 向量相乘xyz
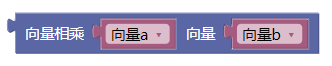
- 3.11. 向量相乘ab
- 3.12. 向量相除xyz
- 3.13. 向量相除ab
- 3.14. 向量长度
- 3.15. 向量长度平方
- 3.16. 向量缩放
- 3.17. 向量设置长度
- 3.18. 向量内积xyz
- 3.19. 向量内积ab
- 3.20. 向量外积xyz
- 3.21. 向量外积ab
- 3.22. 向量欧式距离xyz
- 3.23. 向量欧式距离ab
- 3.24. 向量归一化
- 3.25. 向量归一化结果
- 3.26. 向量角度
- 3.27. 设置向量角度
- 3.28. 向量旋转弧度
- 3.29. 向量旋转弧度(计算)
- 3.30. 向量夹角
- 3.31. 向量插值xyz
- 3.32. 向量插值ab
- 3.33. 向量反射
- 3.34. 向量的数组
- 3.35. 向量相等xyz
- 3.36. 创建二维向量角度
- 3.37. 创建三维向量角度
- 3.38. 随机二维向量
- 3.39. 随机三维向量
- 3.40. 向量的xyz
- 3.41. 向量部分赋值
- 3.42. 向量长度
- 3.43. 调试向量
- 4. 矩阵
- 5. 噪声
- 6. 随机
- 7. 三角学
- 8. 信号
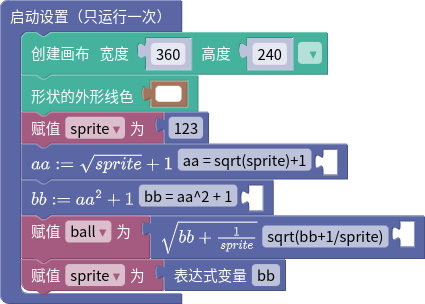
1. 表达式
mathlive表达式和mathjs表达式
2.1. PAI
HALF_PI
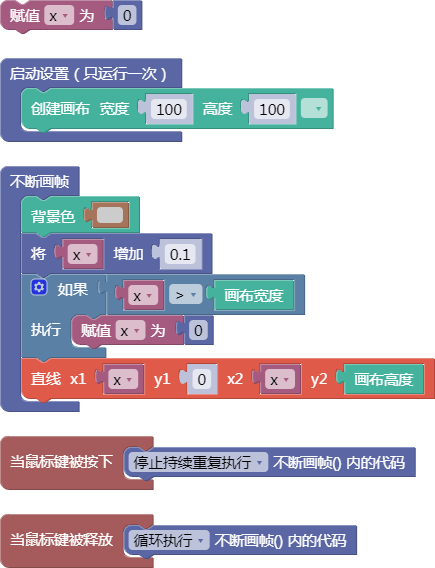
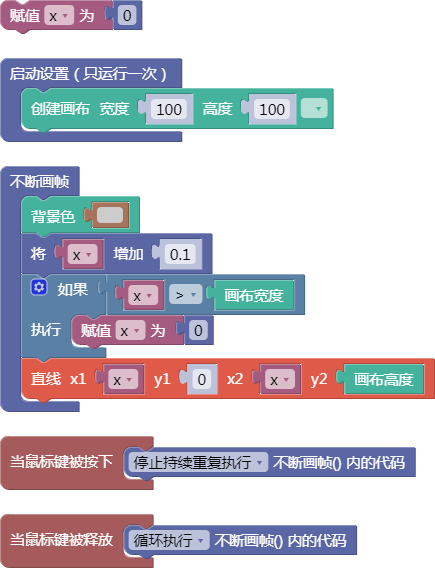
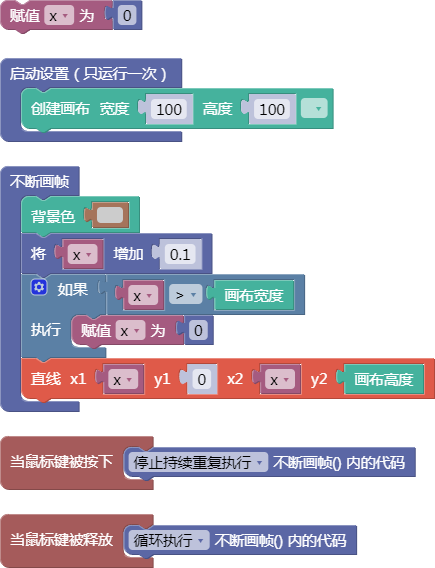
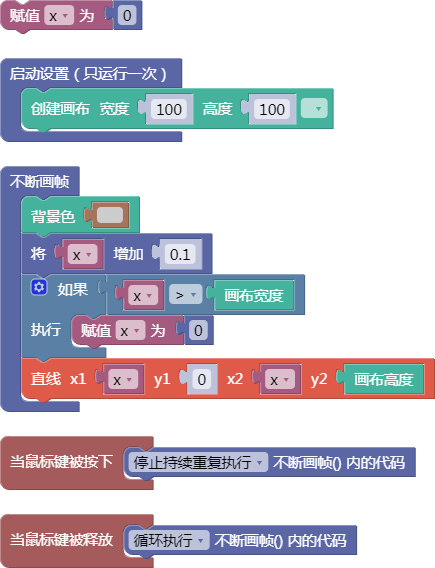
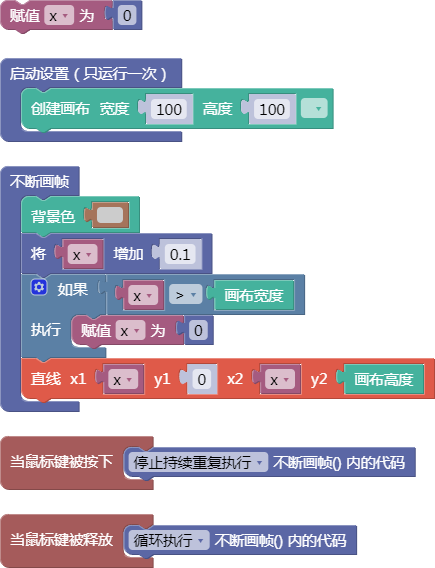
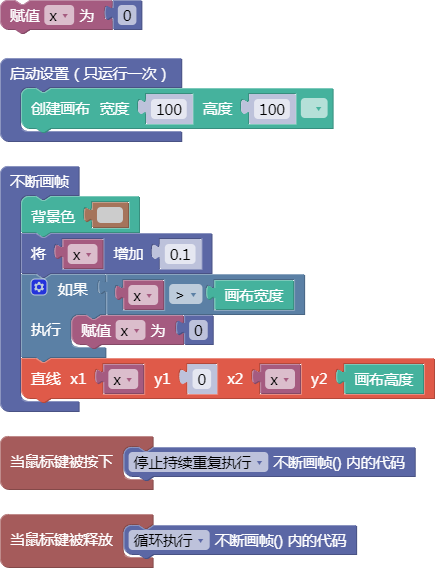
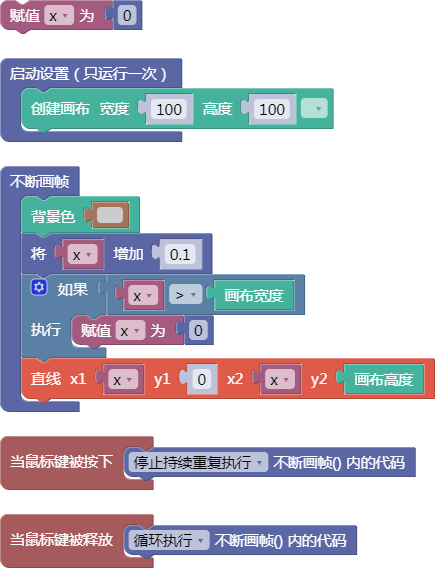
示例:
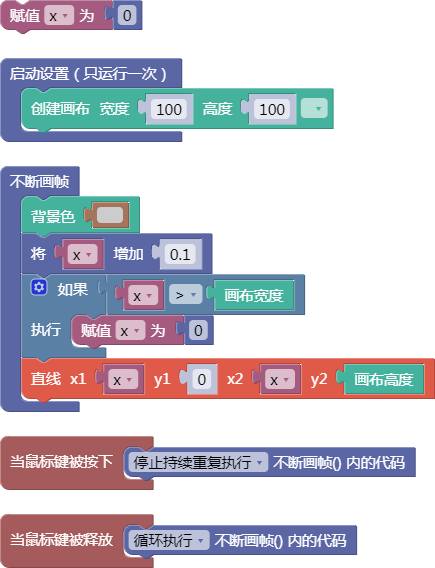
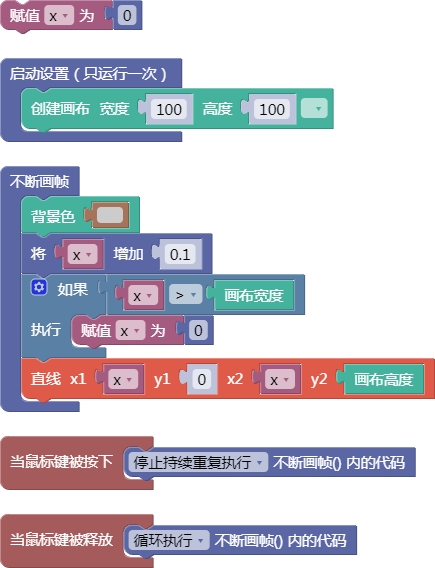
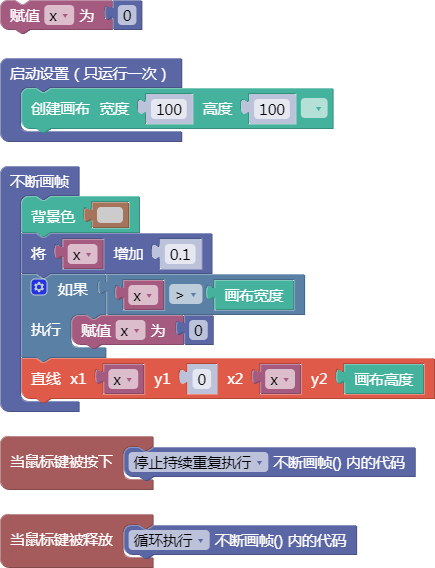
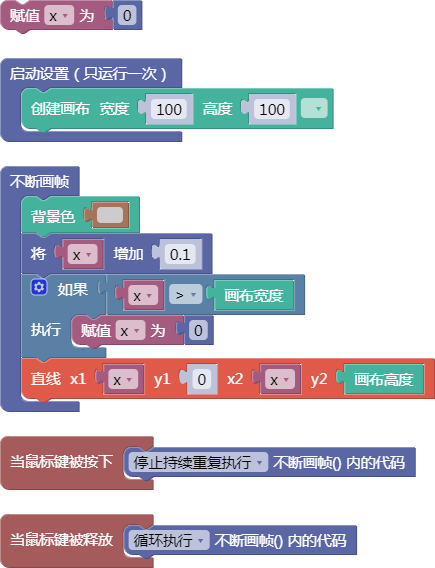
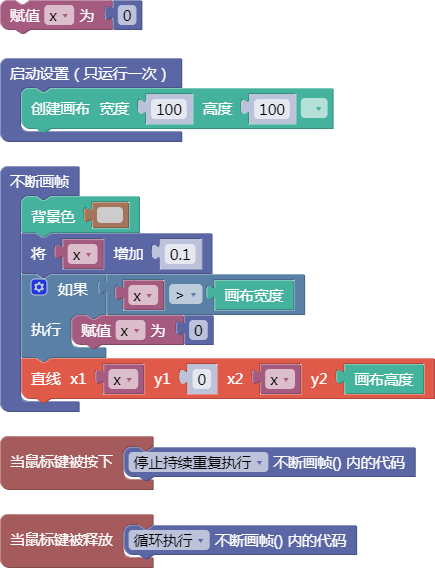
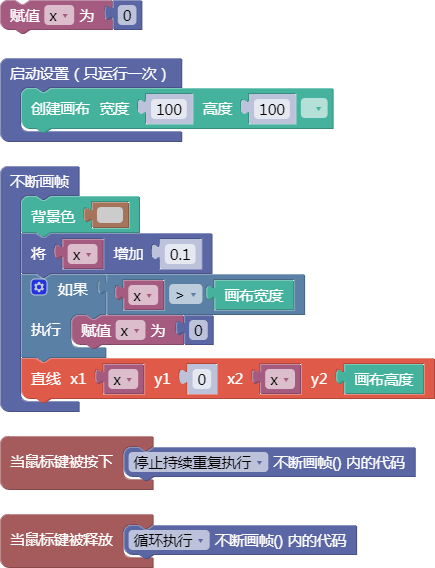
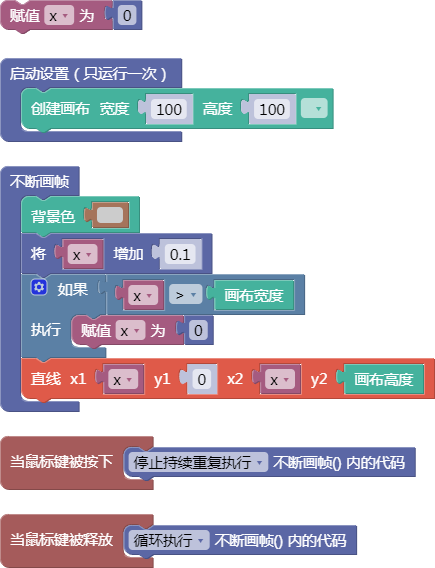
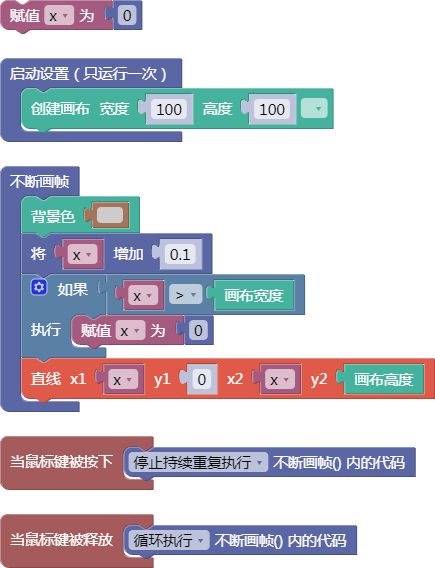
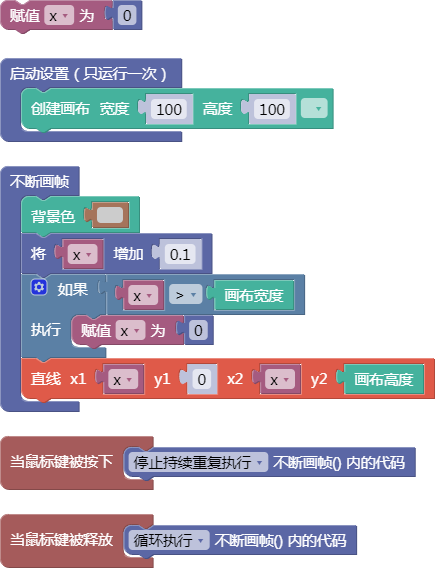
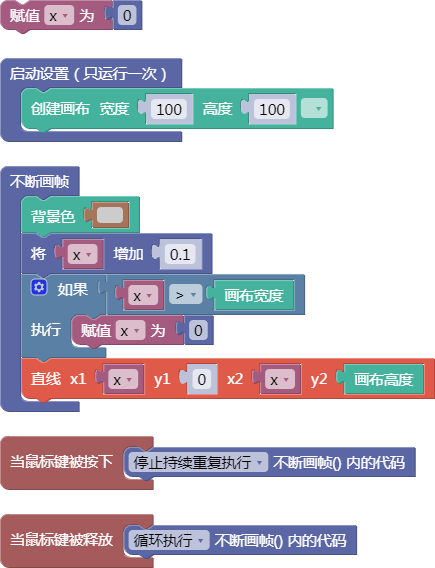
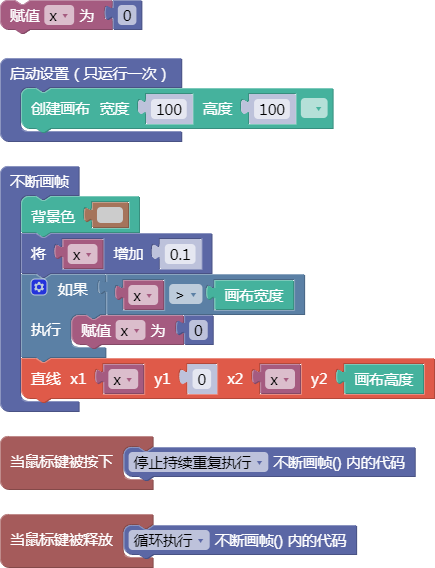
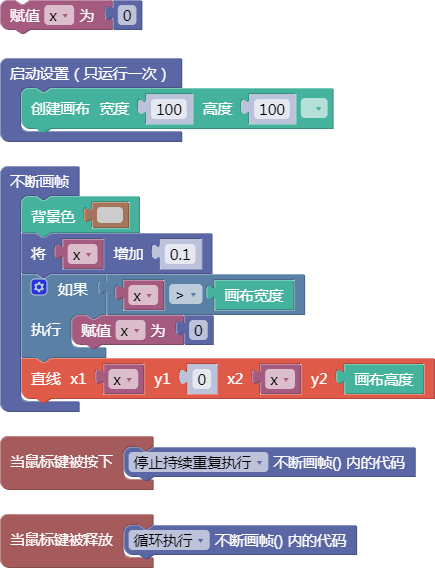
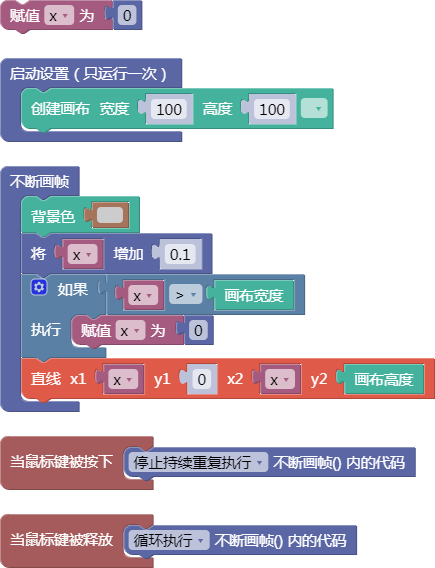
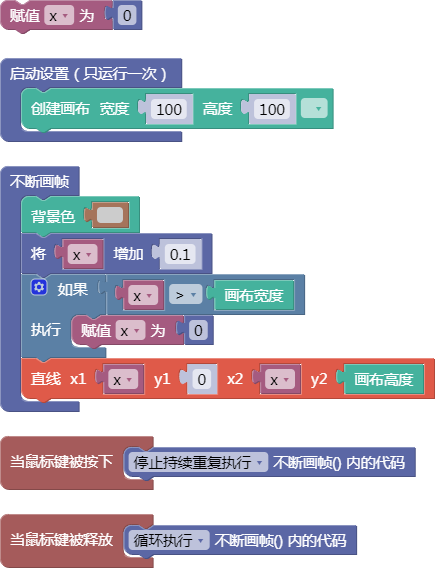
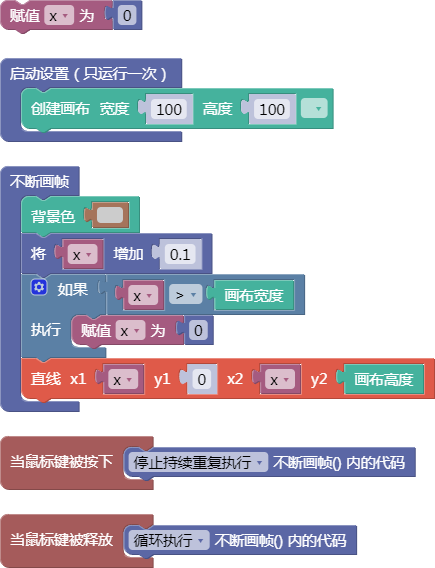
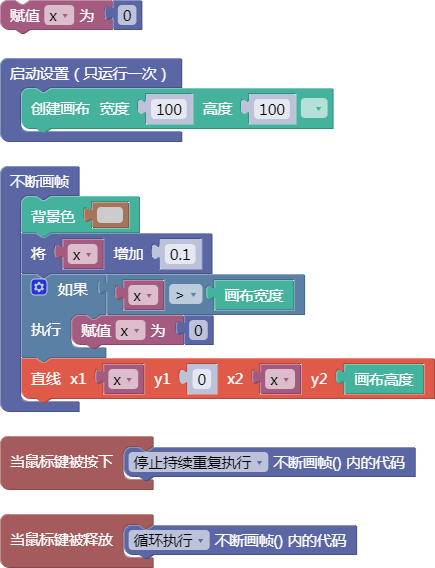
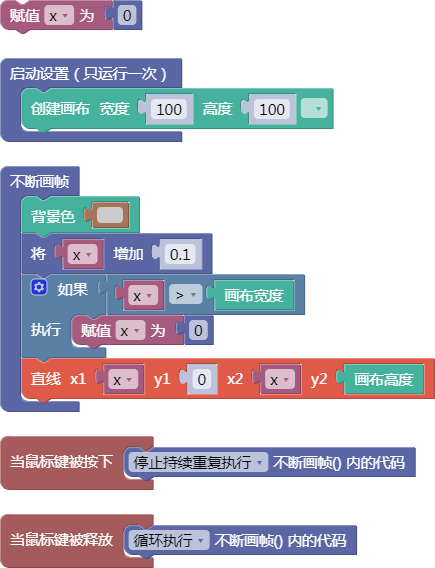
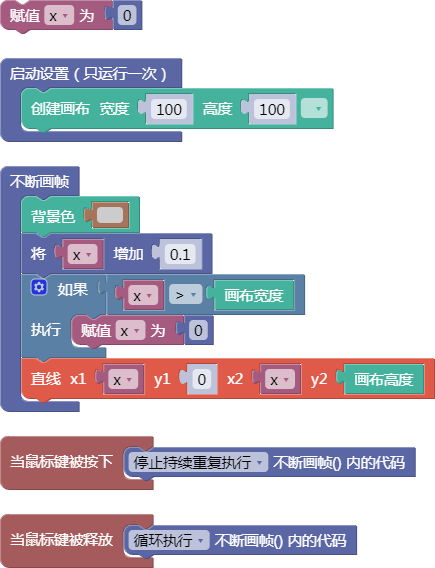
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
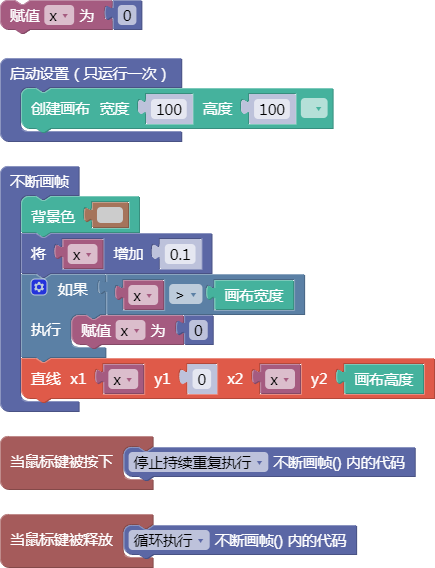
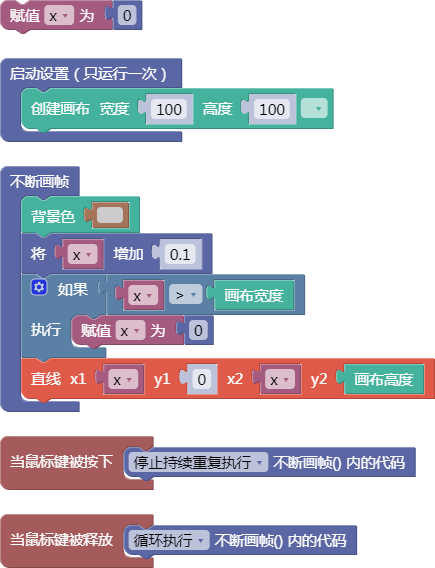
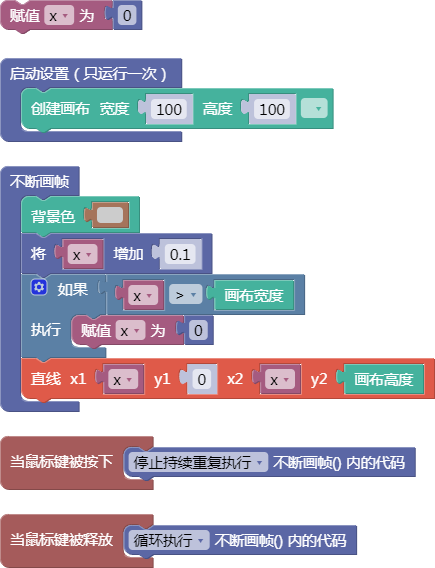
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

2.2. 角度
HALF_PI
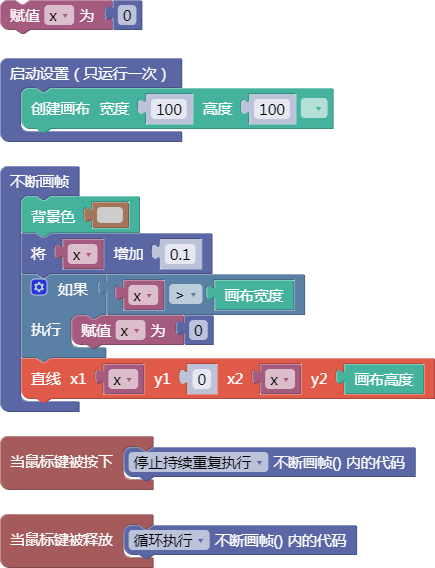
示例:
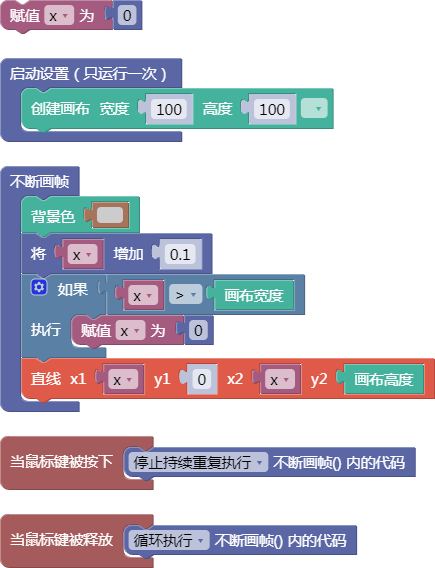
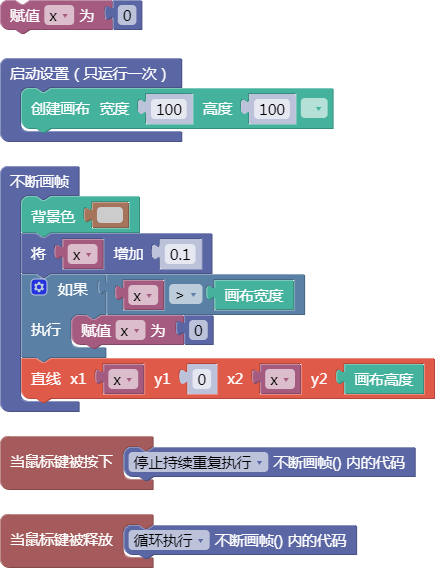
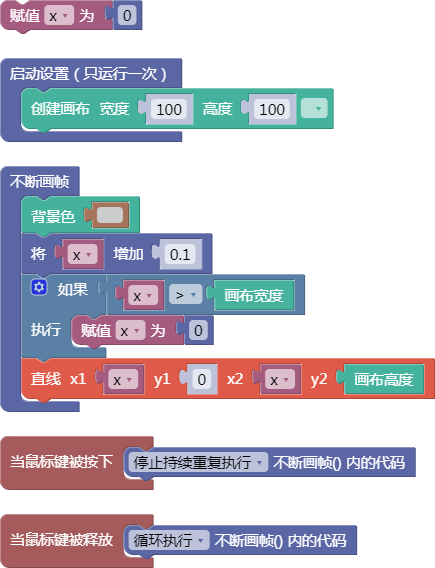
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
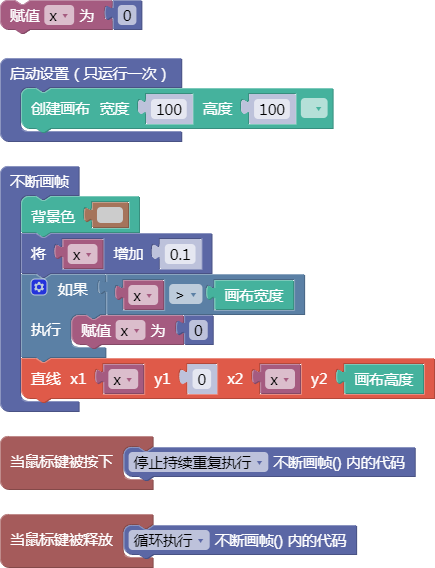
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

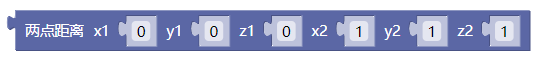
2.3. 两点距离xy
dist()
示例:
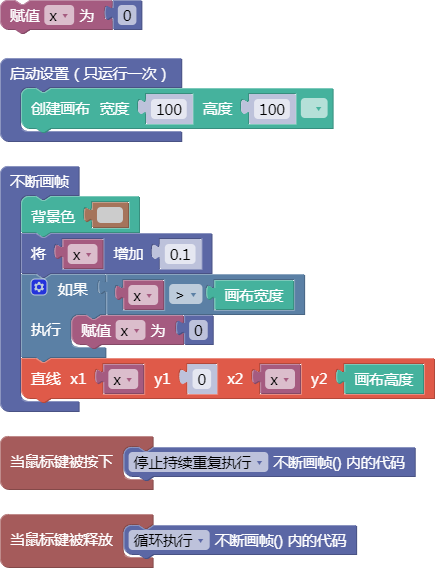
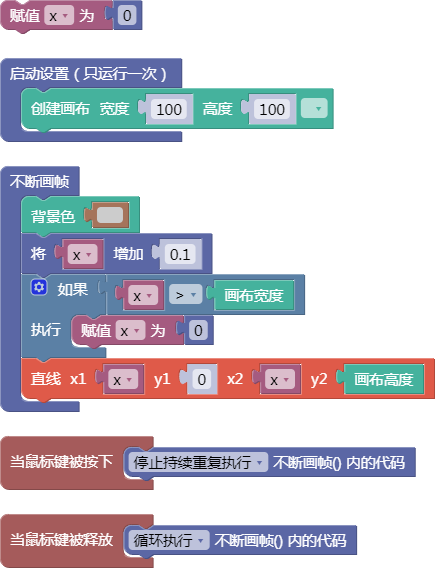
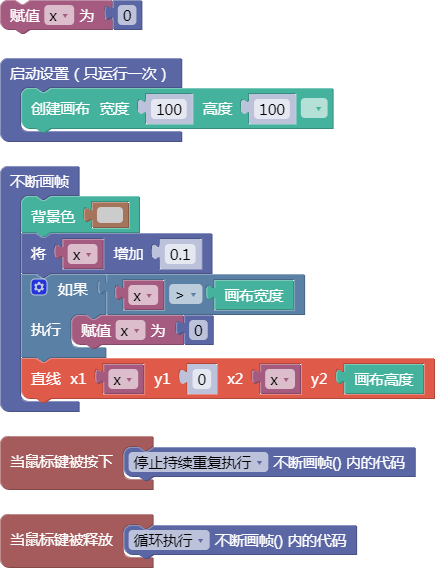
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
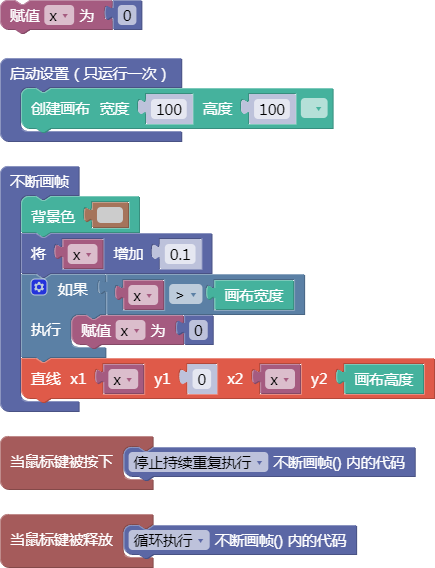
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

2.4. 两点距离xyz
dist()
示例:
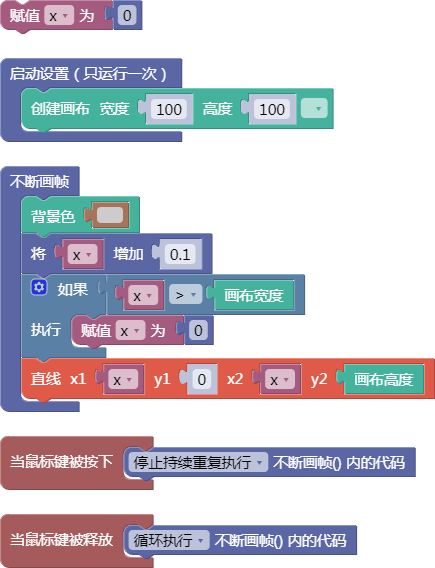
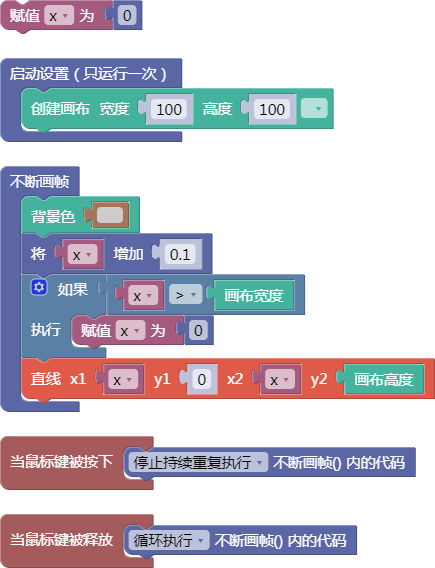
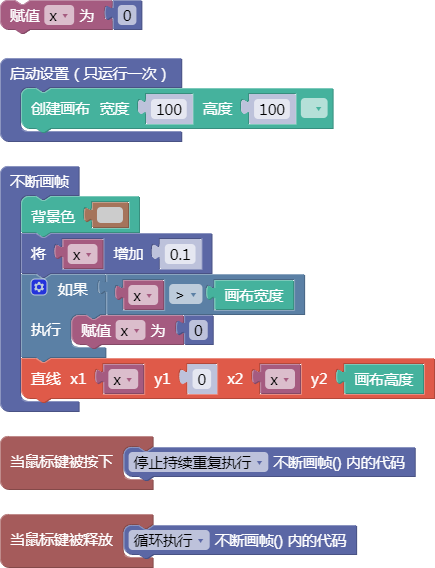
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

2.5. 数值映射
map()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

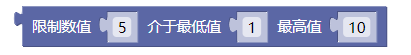
2.6. 限制数值
constrain()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

2.7. 平方
sq()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

2.8. 欧拉数e的指数
exp()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

2.9. 计算插值
lerp()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

3. 向量
3.1. 向量xyz
createVector()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

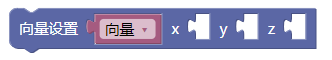
3.2. 向量设置
set()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

3.3. 向量复制
copy()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

3.4. 向量相加xyz
add()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

3.5. 向量相加ab
add()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

3.6. 向量求余xyz
rem()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

3.7. 向量求余ab
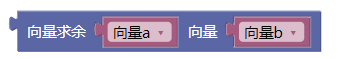
rem()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

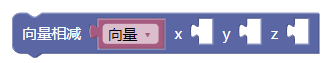
3.8. 向量相减xyz
sub()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

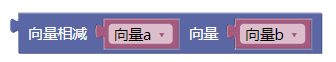
3.9. 向量相减ab
sub()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

3.10. 向量相乘xyz
mult()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

3.11. 向量相乘ab
mult()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

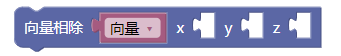
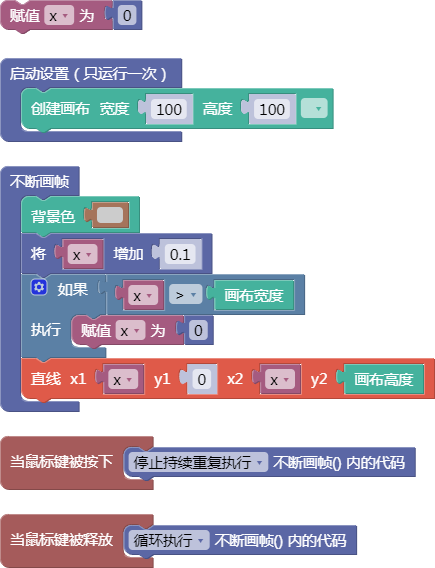
3.12. 向量相除xyz
div()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

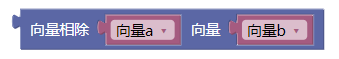
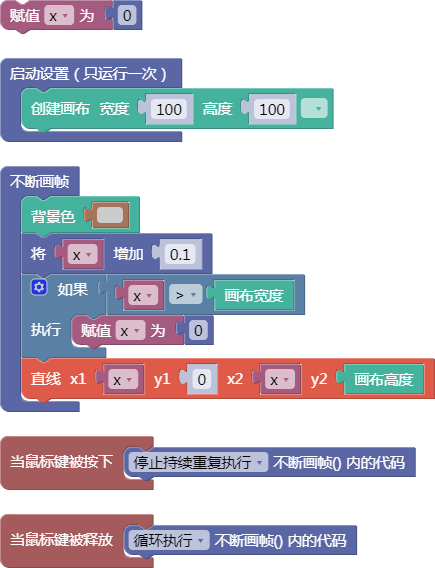
3.13. 向量相除ab
div()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

3.14. 向量长度
mag()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

3.15. 向量长度平方
magSq()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

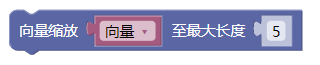
3.16. 向量缩放
limit()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

3.17. 向量设置长度
setMag()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

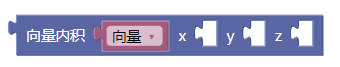
3.18. 向量内积xyz
dot()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

3.19. 向量内积ab
dot()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

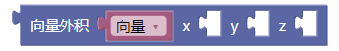
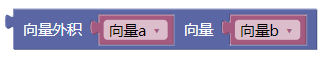
3.20. 向量外积xyz
cross()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

3.21. 向量外积ab
cross()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

3.22. 向量欧式距离xyz
dist()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

3.23. 向量欧式距离ab
dist()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

3.24. 向量归一化
normalize()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

3.25. 向量归一化结果
normalize()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

3.26. 向量角度
heading()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

3.27. 设置向量角度
setHeading()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

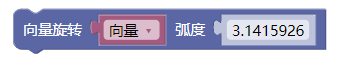
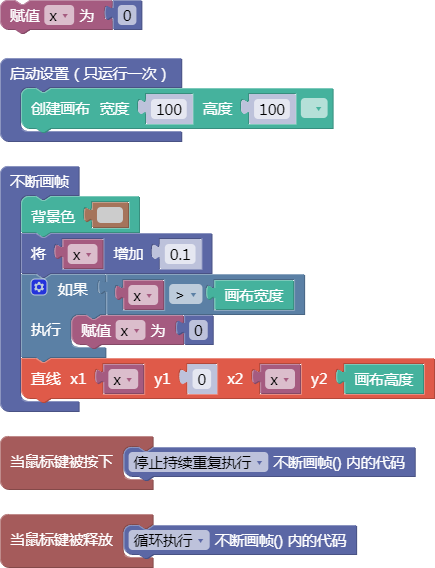
3.28. 向量旋转弧度
rotate()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

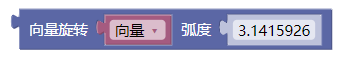
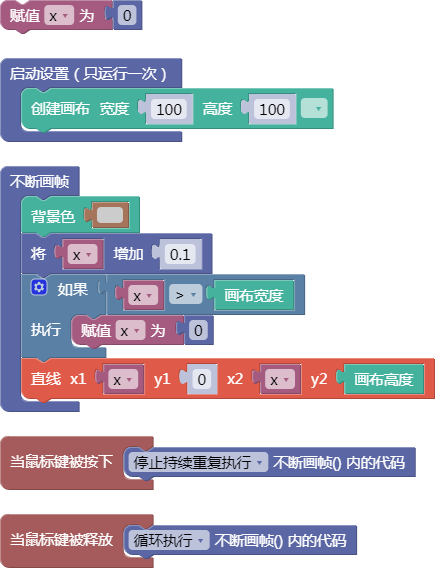
3.29. 向量旋转弧度(计算)
rotate()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

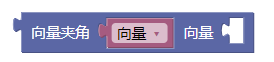
3.30. 向量夹角
angleBetween()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

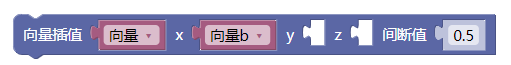
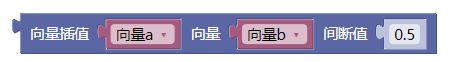
3.31. 向量插值xyz
lerp()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

3.32. 向量插值ab
lerp()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

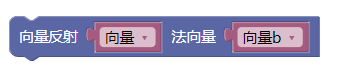
3.33. 向量反射
reflect()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

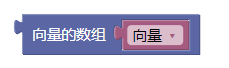
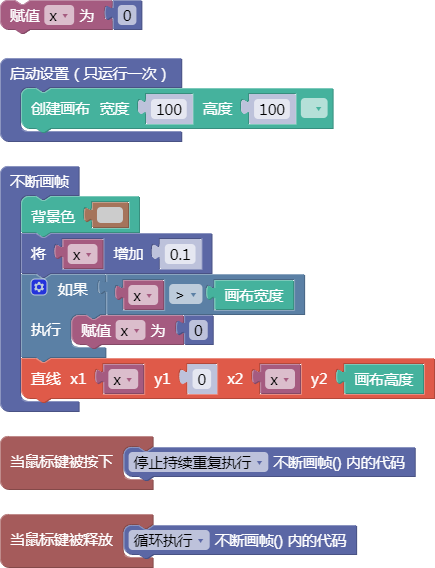
3.34. 向量的数组
array()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

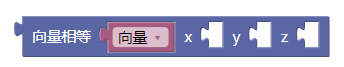
3.35. 向量相等xyz
equals()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

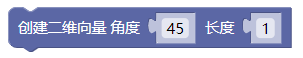
3.36. 创建二维向量角度
fromAngle()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

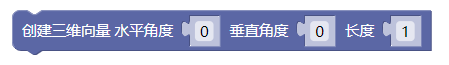
3.37. 创建三维向量角度
fromAngles()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

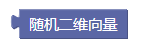
3.38. 随机二维向量
random2D()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

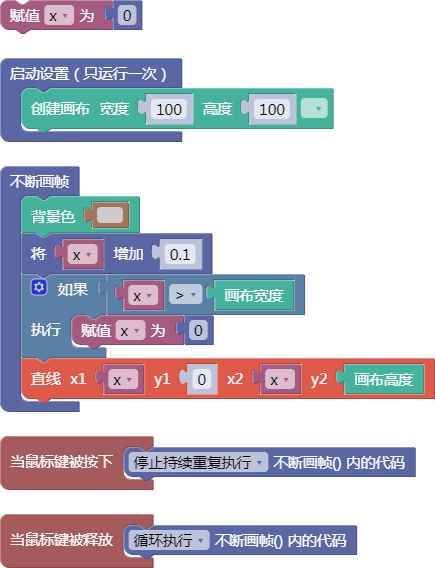
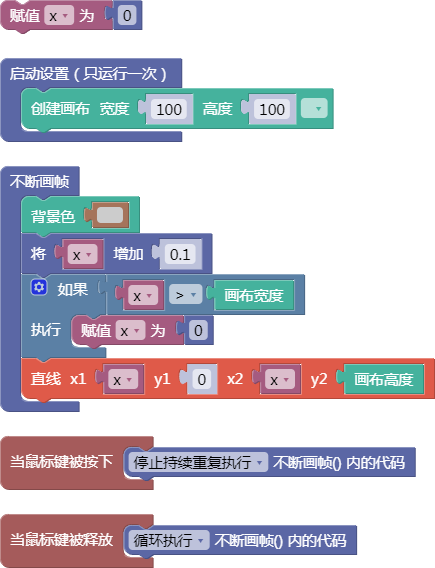
3.39. 随机三维向量
random3D()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

3.40. 向量的xyz
x
y
z
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

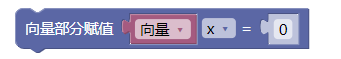
3.41. 向量部分赋值
x
y
z
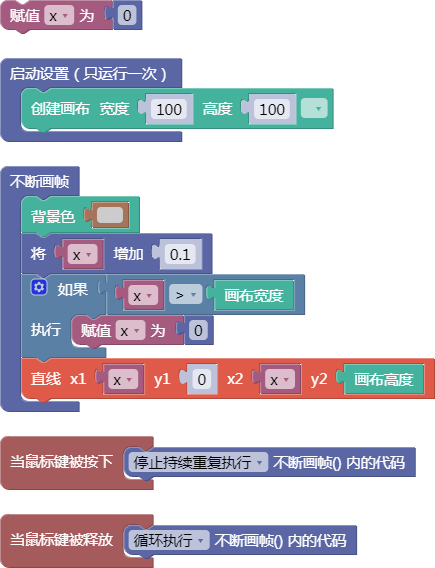
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

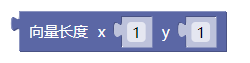
3.42. 向量长度
mag()
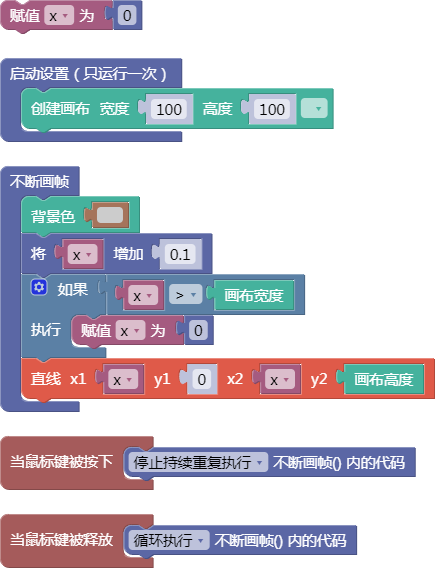
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

3.43. 调试向量
preload()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

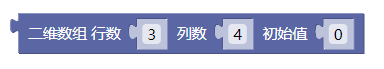
4.1. 二维数组的行列和初始值
preload()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

4.2. 二维数组大小
preload()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

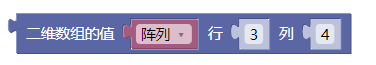
4.3. 二维数组的值行列
preload()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

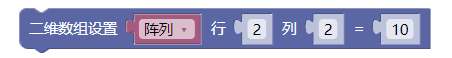
4.4. 二维数组设置
preload()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

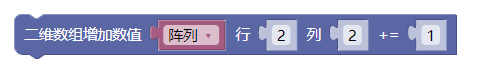
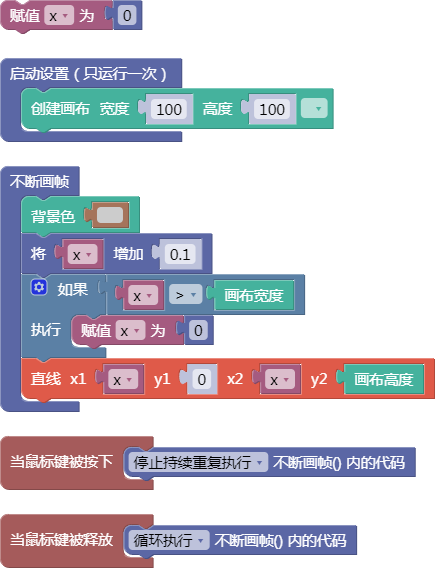
4.5. 二维数组增加数值
preload()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

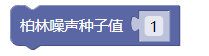
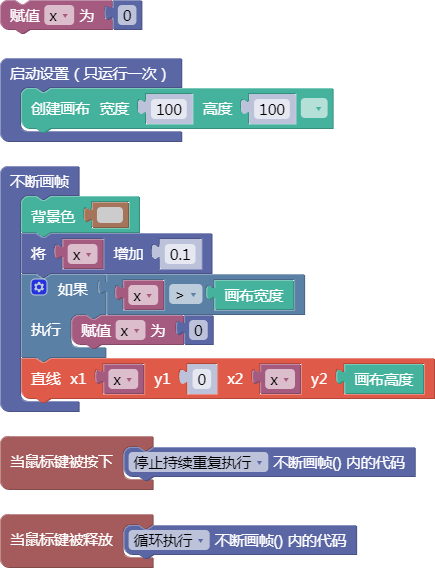
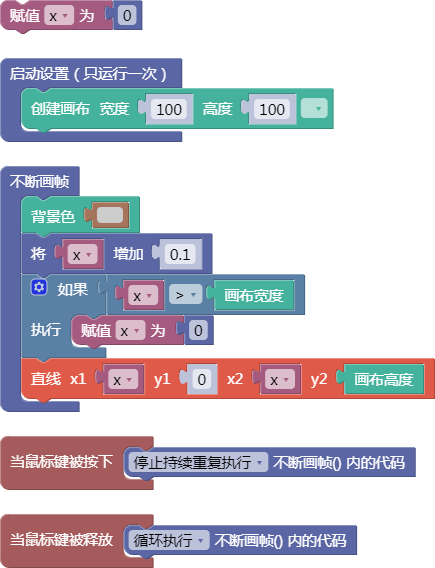
5.1. 柏林噪声种子值
noiseSeed()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

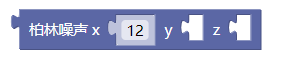
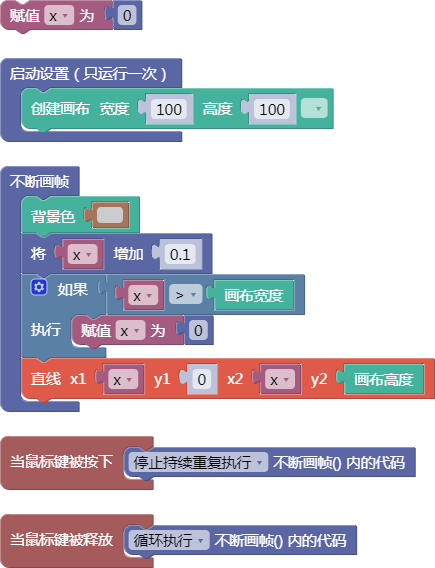
5.2. 柏林噪声xyz
noise()
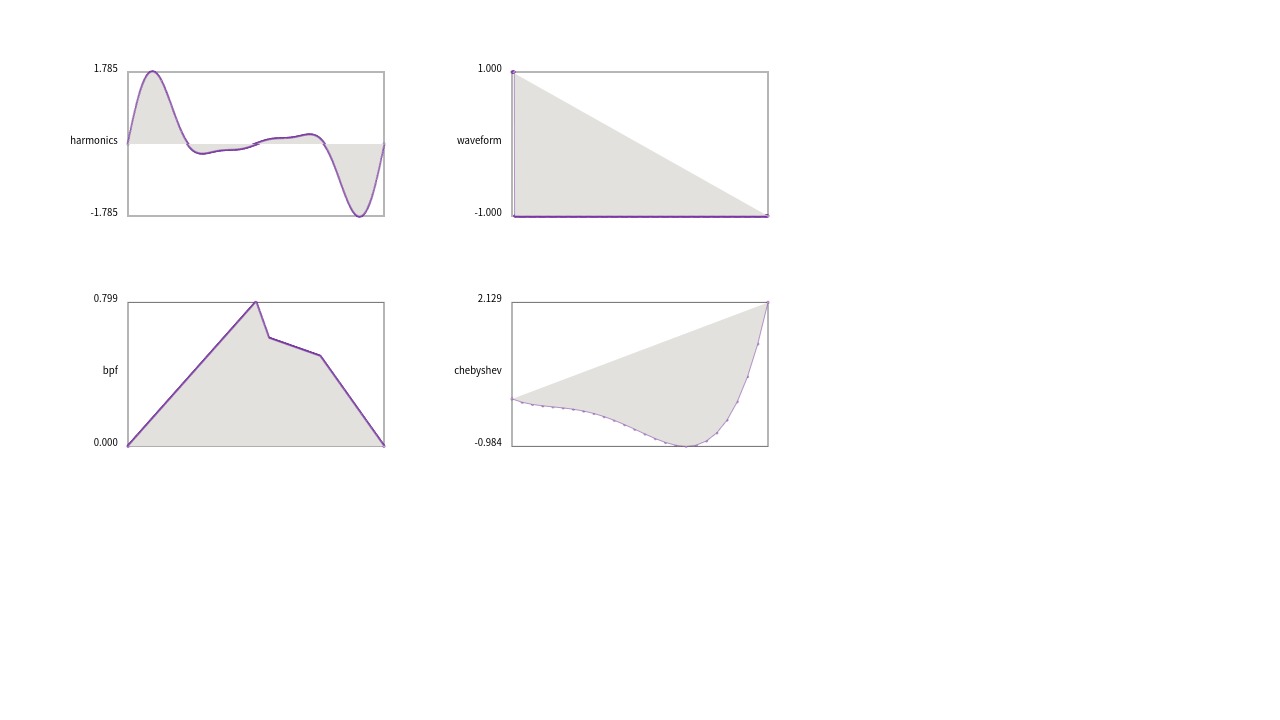
柏林噪声是一个随机序列生成器,与标准的random()函数相比,它产生更自然有序和谐的数字序列。此外,柏林噪声可以在多维空间中定义。关于柏林噪声这个函数更详细的说明可以进一步阅读《代码本色 : 用编程模拟自然系统》(The Nature of Code: Simulating Natural Systems with Processing)这本书引言的部分。
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

5.3. 柏林噪声细节

noiseDetail()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

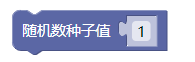
6.1. 随机数种子值
randomSeed()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

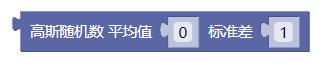
6.2. 高斯随机数
randomGaussian()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

6.3. 随机数
random()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

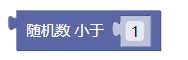
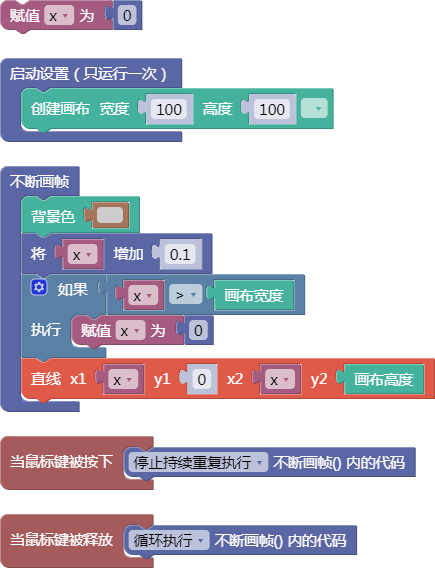
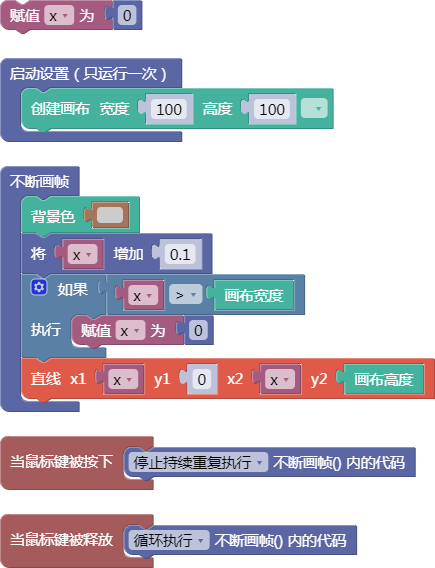
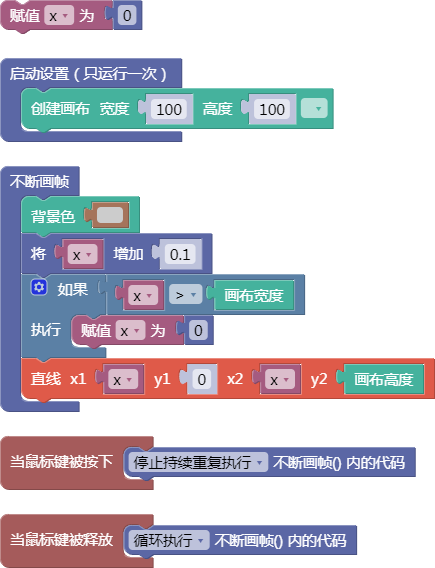
6.4. 随机数小于1
random()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

6.5. 随机数范围
random()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

6.6. 随机整数范围
random()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

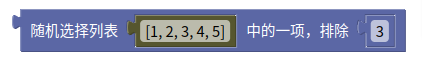
6.8. 随机数数组
random()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

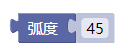
7.1. 弧度
radians()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

7.2. 角度
degrees()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

7.3. 弦函数
preload()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

7.4. 点xy方位角
preload()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下:

7.5. 角度模式
angleMode()
示例:
let x = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(100, 100);
}
function draw() {
background(204);
x = x + 0.1;
if (x > width) {
x = 0;
}
line(x, 0, x, height);
}
function mousePressed() {
noLoop();
}
function mouseReleased() {
loop();
}
舞台区显示的画布内容如下: